Available in: |
Xpress |
Standard |
Expert |
Professional |
Premium |
In order to perform an index 4 Axis Operation, you first need to use the Rotate Table Operation. Here you can index the table to any specified angle and then lock the table in position. This can then be followed by any of the allowable 3 axis machining operations, thereby allowing access to the part from different orientations.
MILL module allows you to create 4 axis index toolpath operations. 4 Axis indexing refers to the ability to rotate the part about the X (A) axis or the Y (B) axis and lock it in position in this new orientation and then perform standard 3 axis milling operations in this locked position. MILL module allows you to program these part rotation motions as well to create standard 3 and 2 ½ axis machining operations in these new part orientations. Indexing is usually performed when you fixture the part in a rotary table. |
In addition to indexed machining of parts, 4 axis continuous machining can be used to machine parts such as rings. 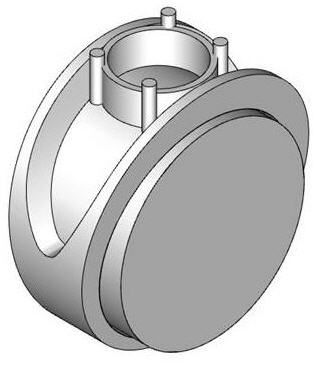 Continuous 4th Axis Machining Operations |
The part shown above is a design of a ring. It can be machined using MILL module's continuous 4 axis machining mode. In the continuous mode, the tool axis is always pointed normal to the rotation axis of the machine tool. In this particular case, the rotary axis of the 4 axis table will be about the X axis. As the part is held such that it spins about the X axis the tool will move about the X and the Z axis simultaneously to perform the machining. This type of machining is called continuous 4 axis machining and can be employed to efficiently machine such parts. |